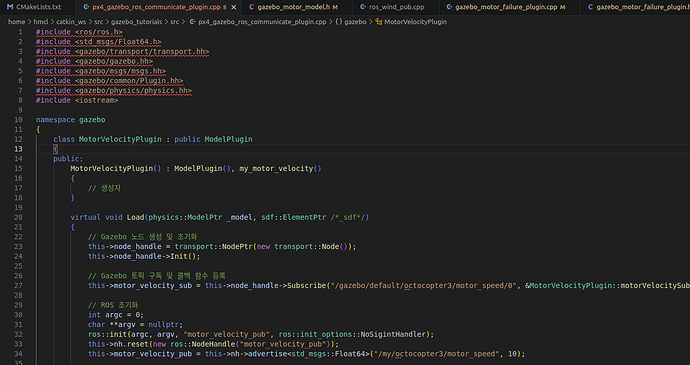
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <std_msgs/Float64.h>
#include <gazebo/transport/transport.hh>
#include <gazebo/gazebo.hh>
#include <gazebo/msgs/msgs.hh>
#include <gazebo/common/Plugin.hh>
#include <gazebo/physics/physics.hh>
#include <iostream>
namespace gazebo
{
class MotorVelocityPlugin : public ModelPlugin
{
public:
MotorVelocityPlugin() : ModelPlugin(), my_motor_velocity()
{
// 생성자
}
virtual void Load(physics::ModelPtr _model, sdf::ElementPtr /*_sdf*/)
{
// Gazebo 노드 생성 및 초기화
this->node_handle = transport::NodePtr(new transport::Node());
this->node_handle->Init();
// Gazebo 토픽 구독 및 콜백 함수 등록
this->motor_velocity_sub = this->node_handle->Subscribe("/gazebo/default/octocopter3/motor_speed/0", &MotorVelocityPlugin::motorVelocitySubCallback, this);
// ROS 초기화
int argc = 0;
char **argv = nullptr;
ros::init(argc, argv, "motor_velocity_pub", ros::init_options::NoSigintHandler);
this->nh.reset(new ros::NodeHandle("motor_velocity_pub"));
this->motor_velocity_pub = this->nh->advertise<std_msgs::Float64>("/my/octocopter3/motor_speed", 10);
// 업데이트 함수 등록
this->updateConnection = event::Events::ConnectWorldUpdateBegin(std::bind(&MotorVelocityPlugin::OnUpdate, this));
}
void motorVelocitySubCallback(const boost::shared_ptr<const gazebo::msgs::Any> &msg)
{
// 메시지에 double 값이 있는지 확인
if (msg->has_double_value())
{
this->my_motor_velocity.data = msg->double_value();
ROS_INFO("Received motor velocity: %f", this->my_motor_velocity.data);
}
else
{
ROS_WARN("Received a message that does not contain a double value.");
}
}
void OnUpdate()
{
// ROS 메시지 퍼블리시
this->motor_velocity_pub.publish(this->my_motor_velocity);
}
private:
transport::NodePtr node_handle; // Gazebo 노드 핸들
transport::SubscriberPtr motor_velocity_sub; // Gazebo 구독자
std::unique_ptr<ros::NodeHandle> nh; // ROS 노드 핸들
ros::Publisher motor_velocity_pub; // ROS 퍼블리셔
std_msgs::Float64 my_motor_velocity; // ROS 메시지
event::ConnectionPtr updateConnection; // Gazebo 업데이트 연결
};
// 플러그인 등록
GZ_REGISTER_MODEL_PLUGIN(MotorVelocityPlugin)
}
The code above is in the path /home/hmcl/catkin_ws/src/gazebo_tutorials/src/px4_gazebo_ros_communicate_plugin.cpp.
/*
* Copyright 2015 Fadri Furrer, ASL, ETH Zurich, Switzerland
* Copyright 2015 Michael Burri, ASL, ETH Zurich, Switzerland
* Copyright 2015 Mina Kamel, ASL, ETH Zurich, Switzerland
* Copyright 2015 Janosch Nikolic, ASL, ETH Zurich, Switzerland
* Copyright 2015 Markus Achtelik, ASL, ETH Zurich, Switzerland
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
#include "gazebo_motor_model.h"
#include <ignition/math.hh>
namespace gazebo
{
GazeboMotorModel::~GazeboMotorModel()
{
updateConnection_->~Connection();
use_pid_ = false;
}
void GazeboMotorModel::InitializeParams() {}
void GazeboMotorModel::Publish()
{
turning_velocity_msg_.set_data(joint_->GetVelocity(0));
// std::cout << "motor_velocity_pub_ to: " << turning_velocity_msg_.data() << " "<< a++ << std::endl;
// GetVelocity(0) 메서드는 해당 조인트의 첫 번째 축(0번 인덱스)에 대한 현재 속도를 반환합니다.
// 반환된 현재 속도를 turning_velocity_msg_ 객체에 넣는다.
// FIXME: Commented out to prevent warnings about queue limit reached.
motor_velocity_pub_->Publish(turning_velocity_msg_); // 이부분 수정했다
// 신기하다
// motor_velocity_pub_ 가 pub하는 토픽에 turning_velocity_msg_ 라는 msg객체의 데이터를 담을수 있다??
}
// Load(physics::ModelPtr _model, sdf::ElementPtr _sdf)는 필수 구성요소다
void GazeboMotorModel::Load(physics::ModelPtr _model, sdf::ElementPtr _sdf)
{
model_ = _model;
namespace_.clear();
if (_sdf->HasElement("robotNamespace"))
namespace_ = _sdf->GetElement("robotNamespace")->Get<std::string>();
else
gzerr << "[gazebo_motor_model] Please specify a robotNamespace.\n";
////Gazebo의 transport 시스템은 시뮬레이션 내의 다양한 컴포넌트 간에 메시지 기반 통신을 가능하게 하는 매커니즘이다
/*
이는 Gazebo 내에서의 데이터 교환과 이벤트 처리를 위한 중요한 구조적 요소입니다.
따라서 node_handle_은 Gazebo 환경에 특화된 노드로, Gazebo 시뮬레이션 밖에서는 사용되지 않습니다.
*/
node_handle_ = transport::NodePtr(new transport::Node());
node_handle_->Init(namespace_);
if (_sdf->HasElement("jointName"))
joint_name_ = _sdf->GetElement("jointName")->Get<std::string>();
else
gzerr << "[gazebo_motor_model] Please specify a jointName, where the rotor is attached.\n";
// Get the pointer to the joint.
joint_ = model_->GetJoint(joint_name_);
if (joint_ == NULL)
gzthrow("[gazebo_motor_model] Couldn't find specified joint \"" << joint_name_ << "\".");
// setup joint control pid to control joint
if (_sdf->HasElement("joint_control_pid"))
{
sdf::ElementPtr pid = _sdf->GetElement("joint_control_pid");
double p = 0.1;
if (pid->HasElement("p"))
p = pid->Get<double>("p");
double i = 0;
if (pid->HasElement("i"))
i = pid->Get<double>("i");
double d = 0;
if (pid->HasElement("d"))
d = pid->Get<double>("d");
double iMax = 0;
if (pid->HasElement("iMax"))
iMax = pid->Get<double>("iMax");
double iMin = 0;
if (pid->HasElement("iMin"))
iMin = pid->Get<double>("iMin");
double cmdMax = 3;
if (pid->HasElement("cmdMax"))
cmdMax = pid->Get<double>("cmdMax");
double cmdMin = -3;
if (pid->HasElement("cmdMin"))
cmdMin = pid->Get<double>("cmdMin");
pid_.Init(p, i, d, iMax, iMin, cmdMax, cmdMin);
use_pid_ = true;
}
else
{
use_pid_ = false;
}
if (_sdf->HasElement("linkName"))
link_name_ = _sdf->GetElement("linkName")->Get<std::string>();
else
gzerr << "[gazebo_motor_model] Please specify a linkName of the rotor.\n";
link_ = model_->GetLink(link_name_);
if (link_ == NULL)
gzthrow("[gazebo_motor_model] Couldn't find specified link \"" << link_name_ << "\".");
if (_sdf->HasElement("motorNumber"))
motor_number_ = _sdf->GetElement("motorNumber")->Get<int>();
else
gzerr << "[gazebo_motor_model] Please specify a motorNumber.\n";
if (_sdf->HasElement("turningDirection"))
{
std::string turning_direction = _sdf->GetElement("turningDirection")->Get<std::string>();
if (turning_direction == "cw")
turning_direction_ = turning_direction::CW;
else if (turning_direction == "ccw")
turning_direction_ = turning_direction::CCW;
else
gzerr << "[gazebo_motor_model] Please only use 'cw' or 'ccw' as turningDirection.\n";
}
else
gzerr << "[gazebo_motor_model] Please specify a turning direction ('cw' or 'ccw').\n";
if (_sdf->HasElement("reversible"))
{
reversible_ = _sdf->GetElement("reversible")->Get<bool>();
}
// std::string: 이는 템플릿 파라미터로, 읽어올 파라미터 값의 타입을 지정합니다. 여기서는 문자열 타입의 파라미터 값을 읽어옵니다.
//_sdf: 이는 파라미터 값을 읽어올 SDF 요소를 가리킵니다. 이는 함수가 호출될 때 함수에 전달되는 SDF 객체입니다.
//"commandSubTopic": 이는 _sdf 요소 내에서 찾고자 하는 파라미터의 이름입니다.
// command_sub_topic_: 이는 파라미터 값을 저장할 변수입니다. 파라미터가 발견되면, 해당 값이 이 변수에 저장됩니다.
// command_sub_topic_: 또는 이 변수의 현재 값은 파라미터가 발견되지 않았을 때 사용될 기본값으로도 기능합니다.
// sdf 파일에서 commandSubTopic의 줄에서 /gazebo/command/motor_speed 내용을 command_sub_topic_에 저장한다.
// 한줄 요약 command_sub_topic_ 에 /gazebo/command/motor_speed 라는 내용 담김
getSdfParam<std::string>(_sdf, "commandSubTopic", command_sub_topic_, command_sub_topic_);
// 한줄 요약 motor_speed_pub_topic_ 에 /motor_speed/0 라는 내용 담김
getSdfParam<std::string>(_sdf, "motorSpeedPubTopic", motor_speed_pub_topic_,
motor_speed_pub_topic_);
getSdfParam<std::string>(_sdf, "ROSMotorNumSubTopic", motor_failure_sub_topic_, motor_failure_sub_topic_); // 내가 추가한거 --------------
getSdfParam<std::string>(_sdf, "ROSMotorNumSubTopic1", motor_failure_sub_topic_1, motor_failure_sub_topic_1); // 내가 추가한거 --------------
getSdfParam<std::string>(_sdf, "ROSMotorNumSubTopic2", motor_failure_sub_topic_2, motor_failure_sub_topic_2); // 내가 추가한거 --------------
getSdfParam<std::string>(_sdf, "ROSMotorNumSubTopic3", motor_failure_sub_topic_3, motor_failure_sub_topic_3); // 내가 추가한거 --------------
getSdfParam<double>(_sdf, "rotorDragCoefficient", rotor_drag_coefficient_, rotor_drag_coefficient_);
getSdfParam<double>(_sdf, "rollingMomentCoefficient", rolling_moment_coefficient_,
rolling_moment_coefficient_);
getSdfParam<double>(_sdf, "maxRotVelocity", max_rot_velocity_, max_rot_velocity_);
getSdfParam<double>(_sdf, "motorConstant", motor_constant_, motor_constant_);
getSdfParam<double>(_sdf, "momentConstant", moment_constant_, moment_constant_);
getSdfParam<double>(_sdf, "timeConstantUp", time_constant_up_, time_constant_up_);
getSdfParam<double>(_sdf, "timeConstantDown", time_constant_down_, time_constant_down_);
getSdfParam<double>(_sdf, "rotorVelocitySlowdownSim", rotor_velocity_slowdown_sim_, 10);
/*
std::cout << "Subscribing to: " << motor_test_sub_topic_ << std::endl;
motor_sub_ = node_handle_->Subscribe<mav_msgs::msgs::MotorSpeed>("~/" + model_->GetName() + motor_test_sub_topic_, &GazeboMotorModel::testProto, this);
*/
// Set the maximumForce on the joint. This is deprecated from V5 on, and the joint won't move.
#if GAZEBO_MAJOR_VERSION < 5
joint_->SetMaxForce(0, max_force_);
#endif
// Listen to the update event. This event is broadcast every
// simulation iteration.
updateConnection_ = event::Events::ConnectWorldUpdateBegin(boost::bind(&GazeboMotorModel::OnUpdate, this, _1));
command_sub_ = node_handle_->Subscribe<mav_msgs::msgs::CommandMotorSpeed>("~/" + model_->GetName() + command_sub_topic_, &GazeboMotorModel::VelocityCallback, this);
std::cout << "[gazebo_motor_model]: Subscribe to gz topic: " << motor_failure_sub_topic_ << std::endl; // 내가 수정 ---------------------
std::cout << "[gazebo_motor_model]: Subscribe to gz topic: " << motor_failure_sub_topic_1 << std::endl; // 내가 수정 ---------------------
std::cout << "[gazebo_motor_model]: Subscribe to gz topic: " << motor_failure_sub_topic_2 << std::endl; // 내가 수정 ---------------------
std::cout << "[gazebo_motor_model]: Subscribe to gz topic: " << motor_failure_sub_topic_3 << std::endl; // 내가 수정 ---------------------
// motor_failure_sub_: 이는 구독자 객체를 저장하기 위한 변수입니다. 이 변수를 통해 생성된 구독자와의 상호작용이 이루어집니다.
// node_handle_: Gazebo에서 통신을 관리하기 위한 노드 핸들 객체입니다. Subscribe 메서드를 호출하여 새로운 구독자를 생성합니다.
// Subscribe<msgs::Int>: Subscribe 메서드는 특정 타입의 메시지에 대한 구독자를 생성합니다. 여기서 <msgs::Int>는 구독할 메시지의 타입을 지정합니다.
// Subscribe<msgs::Int>: 이 경우 msgs::Int 타입의 메시지를 구독하겠다는 의미입니다. msgs::Int는 정수 값을 담을 수 있는 메시지 타입입니다.
// motor_failure_sub_topic_: 구독할 토픽의 이름을 나타내는 문자열 변수입니다. 이 변수에 저장된 이름의 토픽에 대한 메시지가 발행될 때마다 지정된 콜백 함수가 호출됩니다.
// this: 콜백 함수가 속한 객체의 포인터입니다. this 키워드는 현재 인스턴스를 가리키며, 여기서는 GazeboMotorModel 객체 자신을 의미합니다. 약간 self그런건가??
motor_failure_sub_ = node_handle_->Subscribe<msgs::Int>("/gazebo/motor_failure_num", &GazeboMotorModel::MotorFailureCallback, this); // 이부분은 수정했다 //내가 수정한거---------
motor_failure_sub_1 = node_handle_->Subscribe<msgs::Int>("/gazebo/motor_failure_num1", &GazeboMotorModel::MotorFailureCallback1, this); // 이부분은 수정했다 //내가 수정한거---------
motor_failure_sub_2 = node_handle_->Subscribe<msgs::Int>("/gazebo/motor_failure_num2", &GazeboMotorModel::MotorFailureCallback2, this); // 이부분은 수정했다 //내가 수정한거---------
motor_failure_sub_3 = node_handle_->Subscribe<msgs::Int>("/gazebo/motor_failure_num3", &GazeboMotorModel::MotorFailureCallback3, this); // 이부분은 수정했다 //내가 수정한거---------
// FIXME: Commented out to prevent warnings about queue limit reached.
motor_velocity_pub_ = node_handle_->Advertise<std_msgs::msgs::Float>("~/" + model_->GetName() + motor_speed_pub_topic_, 10); // 이부분 수정했다
wind_sub_ = node_handle_->Subscribe<physics_msgs::msgs::Wind>("~/world_wind", &GazeboMotorModel::WindVelocityCallback, this); // 여기에 gazebo_wind_plugin에서 오는 /world_wind가 들어온다.
// Create the first order filter.
rotor_velocity_filter_.reset(new FirstOrderFilter<double>(time_constant_up_, time_constant_down_, ref_motor_rot_vel_));
}
// Protobuf test
/*
void GazeboMotorModel::testProto(MotorSpeedPtr &msg) {
std::cout << "Received message" << std::endl;
std::cout << msg->motor_speed_size()<< std::endl;
for(int i; i < msg->motor_speed_size(); i++){
std::cout << msg->motor_speed(i) <<" ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
*/
// This gets called by the world update start event.
void GazeboMotorModel::OnUpdate(const common::UpdateInfo &_info)
{
sampling_time_ = _info.simTime.Double() - prev_sim_time_;
prev_sim_time_ = _info.simTime.Double();
UpdateForcesAndMoments();
UpdateMotorFail(); // 이부분 수정했다
UpdateMotorFail1(); // 이부분 수정했다
UpdateMotorFail2(); // 이부분 수정했다
UpdateMotorFail3(); // 이부분 수정했다
Publish();
}
void GazeboMotorModel::VelocityCallback(CommandMotorSpeedPtr &rot_velocities)
{
if (rot_velocities->motor_speed_size() < motor_number_)
{
std::cout << "You tried to access index " << motor_number_
<< " of the MotorSpeed message array which is of size " << rot_velocities->motor_speed_size() << "." << std::endl;
}
else
ref_motor_rot_vel_ = std::min(static_cast<double>(rot_velocities->motor_speed(motor_number_)), static_cast<double>(max_rot_velocity_));
}
// const boost::shared_ptr<const msgs::Int> &fail_msg: 이 파라미터는 모터 고장 번호를 담고 있는 메시지의 포인터를 받습니다.
// boost::shared_ptr는 C++의 스마트 포인터 중 하나로, 메모리 관리를 자동으로 처리해주며 여기서는 msgs::Int 타입의 객체를 가리킵니다.
// fail_msg->data()를 호출하여 메시지에서 모터 고장 번호를 추출하고, 이를 motor_Failure_Number_ 멤버 변수에 저장합니다.
// data() 메서드는 msgs::Int 타입의 메시지에서 실제 정수 값을 가져오는 데 사용됩니다.
void GazeboMotorModel::MotorFailureCallback(const boost::shared_ptr<const msgs::Int> &fail_msg)
{ // 이부분 수정했다
// std::cout << "Received motor failure message for motor 1: " << fail_msg->data() << std::endl;
motor_Failure_Number_ = fail_msg->data();
}
void GazeboMotorModel::MotorFailureCallback1(const boost::shared_ptr<const msgs::Int> &fail_msg)
{ // 이부분 수정했다
motor_Failure_Number_1 = fail_msg->data();
}
void GazeboMotorModel::MotorFailureCallback2(const boost::shared_ptr<const msgs::Int> &fail_msg)
{ // 이부분 수정했다
motor_Failure_Number_2 = fail_msg->data();
}
void GazeboMotorModel::MotorFailureCallback3(const boost::shared_ptr<const msgs::Int> &fail_msg)
{ // 이부분 수정했다
motor_Failure_Number_3 = fail_msg->data();
}
void GazeboMotorModel::UpdateForcesAndMoments()
{
motor_rot_vel_ = joint_->GetVelocity(0); // Get the rotation rate of an axis(index)
// motor_rot_vel_ : [rad/s]
// M_PI = 3.141592
// motor_rot_vel_ / (2 * M_PI) : motor_rot_vel의 단위가 [rad/s] 인데 이거를 [Revolution / sec]로 바꾸는것
// aliasing 방지 : 에일리어싱은 샘플링 주파수가 낮으면 실제 데이터의 모든 값을 담을수가 없다.?? 그런거??
if (motor_rot_vel_ / (2 * M_PI) > 1 / (2 * sampling_time_))
{
gzerr << "Aliasing on motor [" << motor_number_ << "] might occur. Consider making smaller simulation time steps or raising the rotor_velocity_slowdown_sim_ param.\n";
}
double real_motor_velocity = motor_rot_vel_ * rotor_velocity_slowdown_sim_;
// motor_rot_vel_: 라디안/초 (rad/s)
// rotor_velocity_slowdown_sim_: 무차원 : 시뮬레이션에서 실제 속도를 반영하기 위한 조정 상수입니다.
// real_motor_velocity: 라디안/초 (rad/s)
// std::cout << "vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv [" << real_motor_velocity << "] " << a++ << std::endl;
// Ct 는 무차원 : thrust coefficient
// F= ma // [N] = [kg][m/s^2]
// motor_constant_ : [kg*m]
double force = real_motor_velocity * std::abs(real_motor_velocity) * motor_constant_;
if (!reversible_)
{
// Not allowed to have negative thrust.
force = std::abs(force);
}
// std::cout << "fffffffffffffff [" << force << "] " << std::endl;
// scale down force linearly with forward speed
// XXX this has to be modelled better
//
#if GAZEBO_MAJOR_VERSION >= 9
/// \brief Get the linear velocity of the origin of the link frame,
/// expressed in the world frame.
/// \return Linear velocity of the link frame.
ignition::math::Vector3d body_velocity = link_->WorldLinearVel();
ignition::math::Vector3d joint_axis = joint_->GlobalAxis(0);
#else
ignition::math::Vector3d body_velocity = ignitionFromGazeboMath(link_->GetWorldLinearVel());
ignition::math::Vector3d joint_axis = ignitionFromGazeboMath(joint_->GetGlobalAxis(0));
#endif
// body_velocity : 각 로터의 world frame 바탕인 velocity를 가지고 있다 옥토는 8개
// 초기에 상태
// [0.000495 0.000687 -0.000855] 4176
// [0.000496 0.000688 0.000617] 4176
// [0.000496 0.000687 0.000516] 4176
// [0.000496 0.000689 0.003256] 4176
// [0.000495 0.000687 -0.003495] 4176
// [0.000496 0.000688 -0.000756] 4176
// [0.000496 0.000687 -0.002127] 4176
// [0.000496 0.000688 0.001886] 4176
// joint_axis : 각 로터의 world frame 바탕인 축을 가져온다.
// [9e-06 0.00067 1] 5548
// [2.6e-05 0.000672 1] 5548
// [1.8e-05 0.000648 1] 5548
// [2.4e-05 0.000648 1] 5548
// [1.1e-05 0.00065 1] 5548
// [3e-05 0.000651 1] 5548
// [9e-06 0.00067 1] 5548
// [2.1e-05 0.000668 1] 5548
ignition::math::Vector3d relative_wind_velocity = body_velocity - wind_vel_;
// std::cout << "hihihihi [" << joint_axis << "] " << a++ << std::endl;
ignition::math::Vector3d velocity_parallel_to_rotor_axis = (relative_wind_velocity.Dot(joint_axis)) * joint_axis;
// velocity_parallel_to_rotor_axis : 로터 축에 평행한 속도 성분을 계산한 값
// std::cout << "hihihihi [" << velocity_parallel_to_rotor_axis << "] " << a++ << std::endl;
// velocity_parallel_to_rotor_axis
// [0.000748 -0.054489 0.604408] 6291
// [0.001442 -0.101861 1.12928] 6291
// [0.002222 -0.055256 0.612941] 6291
// [0.002314 -0.056979 0.631233] 6291
// [0.003897 -0.099503 1.10332] 6291
// [0.004035 -0.101197 1.12119] 6291
// [0.001384 -0.100388 1.11246] 6291
// [0.00071 -0.056189 0.622562] 6291
double vel = velocity_parallel_to_rotor_axis.Length();
double scalar = 1 - vel / 25.0; // at 25 m/s the rotor will not produce any force anymore
scalar = ignition::math::clamp(scalar, 0.0, 1.0);
// Apply a force to the link.
link_->AddRelativeForce(ignition::math::Vector3d(0, 0, force * scalar));
// std::cout << "wwwwwwwwwwwwwww [" << ignition::math::Vector3d(0, 0, force * scalar) << "] " << std::endl;
// Forces from Philppe Martin's and Erwan Salaün's
// 2010 IEEE Conference on Robotics and Automation paper
// The True Role of Accelerometer Feedback in Quadrotor Control
// - \omega * \lambda_1 * V_A^{\perp}
ignition::math::Vector3d velocity_perpendicular_to_rotor_axis = relative_wind_velocity - (relative_wind_velocity.Dot(joint_axis)) * joint_axis;
// velocity_perpendicular_to_rotor_axis : 로터 축에 수직한 바람의 속도 벡터. : 계산하다보니 이거 z축 바람만 영향을 받는듯?
ignition::math::Vector3d air_drag = -std::abs(real_motor_velocity) * rotor_drag_coefficient_ * velocity_perpendicular_to_rotor_axis;
// Apply air_drag to link.
link_->AddForce(air_drag);
// std::cout << "aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa [" << air_drag << "] " << std::endl;
// std::cout << "gggggggggggggggggggg [" << link_->WorldForce() << "] " << std::endl;
// Moments
// Getting the parent link, such that the resulting torques can be applied to it.
physics::Link_V parent_links = link_->GetParentJointsLinks(); // link_->GetParentJointsLinks()를 사용하여 현재 링크에 연결된 부모 링크들을 가져옵니다.
// The tansformation from the parent_link to the link_.
#if GAZEBO_MAJOR_VERSION >= 9
ignition::math::Pose3d pose_difference = link_->WorldCoGPose() - parent_links.at(0)->WorldCoGPose();
// link_->WorldCoGPose(): 현재 링크(rotor)의 질량 중심(World Center of Gravity, CoG) 위치와 자세를 반환합니다.
// parent_links.at(0)->WorldCoGPose(): 부모 링크(base_link p.s sdf파일 참조)의 질량 중심 위치와 자세를 반환합니다.
#else
ignition::math::Pose3d pose_difference = ignitionFromGazeboMath(link_->GetWorldCoGPose() - parent_links.at(0)->GetWorldCoGPose());
#endif
// std::cout << "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx [" << link_->WorldCoGPose() << "] " << std::endl;
// std::cout << "zzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz [" << parent_links.at(0)->WorldCoGPose() << "] " << std::endl;
// const static int CCW = 1;
// const static int CW = -1; drag torque는 힘의 반대로 작용해야하기 때문에 CW 를 -1 로 잡았다.
ignition::math::Vector3d drag_torque(0, 0, -turning_direction_ * force * moment_constant_);
// drag_torque : 동력 전달 계통(동력을 전달하는 장치로서 클러치, 변속기, 추진축, 감속기, 차동기, 후차축 등의 부품)의 회전 저항을 말하며, 부하가 걸려 있지 않은 상태의 동력 전달 계통을 회전시키는 데 필요한 토크를 이른다.
// Transforming the drag torque into the parent frame to handle arbitrary rotor orientations.
// drag_torque_parent_frame는 부모 링크의 프레임에서 표현된 항력 토크 벡터입니다.
ignition::math::Vector3d drag_torque_parent_frame = pose_difference.Rot().RotateVector(drag_torque);
parent_links.at(0)->AddRelativeTorque(drag_torque_parent_frame);
// drag_torque_parent_frame : 역시 힘의 반대방향이 적용된다.
// std::cout << "dddddddddddddd [" << drag_torque_parent_frame << "] " << std::endl;
ignition::math::Vector3d rolling_moment;
// - \omega * \mu_1 * V_A^{\perp}
rolling_moment = -std::abs(real_motor_velocity) * turning_direction_ * rolling_moment_coefficient_ * velocity_perpendicular_to_rotor_axis;
parent_links.at(0)->AddTorque(rolling_moment);
// Apply the filter on the motor's velocity.
double ref_motor_rot_vel;
ref_motor_rot_vel = rotor_velocity_filter_->updateFilter(ref_motor_rot_vel_, sampling_time_);
#if 0 // FIXME: disable PID for now, it does not play nice with the PX4 CI system.
if (use_pid_)
{
double err = joint_->GetVelocity(0) - turning_direction_ * ref_motor_rot_vel / rotor_velocity_slowdown_sim_;
double rotorForce = pid_.Update(err, sampling_time_);
joint_->SetForce(0, rotorForce);
// gzerr << "rotor " << joint_->GetName() << " : " << rotorForce << "\n";
}
else
{
#if GAZEBO_MAJOR_VERSION >= 7
// Not desirable to use SetVelocity for parts of a moving model
// impact on rest of the dynamic system is non-physical.
joint_->SetVelocity(0, turning_direction_ * ref_motor_rot_vel / rotor_velocity_slowdown_sim_);
#elif GAZEBO_MAJOR_VERSION >= 6
// Not ideal as the approach could result in unrealistic impulses, and
// is only available in ODE
joint_->SetParam("fmax", 0, 2.0);
joint_->SetParam("vel", 0, turning_direction_ * ref_motor_rot_vel / rotor_velocity_slowdown_sim_);
#endif
}
#else
joint_->SetVelocity(0, turning_direction_ * ref_motor_rot_vel / rotor_velocity_slowdown_sim_);
// 결국 이게 최종으로 들어가는듯 하다.
// ref_motor_rot_vel / rotor_velocity_slowdown_sim_ 하는 이유는 확실하지 않지만, 시뮬레이션을 고려해서 rotor_velocity_slowdown_sim_ 을 곱했지만
// 모터에 주입할때는 시뮬레이션 고려한 상수인 rotor_velocity_slowdown_sim_ 를 나누고 주입해야한다.
#endif /* if 0 */
}
// 여기서부터는 있는게 없다
void GazeboMotorModel::UpdateMotorFail()
{
if (motor_number_ == motor_Failure_Number_ - 1)
{
// motor_constant_ = 0.0;
joint_->SetVelocity(0, 0);
if (screen_msg_flag)
{
std::cout << "Motor number [" << motor_Failure_Number_ << "] failed! [Motor thrust = 0]" << std::endl;
tmp_motor_num = motor_Failure_Number_;
screen_msg_flag = 0;
}
}
else if (motor_Failure_Number_ == 0 && motor_number_ == tmp_motor_num - 1)
{
if (!screen_msg_flag)
{
// motor_constant_ = kDefaultMotorConstant;
std::cout << "Motor number [" << tmp_motor_num << "] running! [Motor thrust = (default)]" << std::endl;
screen_msg_flag = 1;
}
}
}
void GazeboMotorModel::UpdateMotorFail1()
{
if (motor_number_ == motor_Failure_Number_1 - 1)
{
// motor_constant_ = 0.0;
joint_->SetVelocity(0, 0);
if (screen_msg_flag1)
{
std::cout << "Motor number [" << motor_Failure_Number_1 << "] failed! [Motor thrust = 0]" << std::endl;
tmp_motor_num1 = motor_Failure_Number_1;
screen_msg_flag1 = 0;
}
}
else if (motor_Failure_Number_1 == 0 && motor_number_ == tmp_motor_num1 - 1)
{
if (!screen_msg_flag1)
{
// motor_constant_ = kDefaultMotorConstant;
std::cout << "Motor number [" << tmp_motor_num1 << "] running! [Motor thrust = (default)]" << std::endl;
screen_msg_flag1 = 1;
}
}
}
void GazeboMotorModel::UpdateMotorFail2()
{
if (motor_number_ == motor_Failure_Number_2 - 1)
{
// motor_constant_ = 0.0;
joint_->SetVelocity(0, 0);
if (screen_msg_flag2)
{
std::cout << "Motor number [" << motor_Failure_Number_2 << "] failed! [Motor thrust = 0]" << std::endl;
tmp_motor_num2 = motor_Failure_Number_2;
screen_msg_flag2 = 0;
}
}
else if (motor_Failure_Number_2 == 0 && motor_number_ == tmp_motor_num2 - 1)
{
if (!screen_msg_flag2)
{
// motor_constant_ = kDefaultMotorConstant;
std::cout << "Motor number [" << tmp_motor_num2 << "] running! [Motor thrust = (default)]" << std::endl;
screen_msg_flag2 = 1;
}
}
}
void GazeboMotorModel::UpdateMotorFail3()
{
if (motor_number_ == motor_Failure_Number_3 - 1)
{
// motor_constant_ = 0.0;
joint_->SetVelocity(0, 0);
if (screen_msg_flag3)
{
std::cout << "Motor number [" << motor_Failure_Number_3 << "] failed! [Motor thrust = 0]" << std::endl;
tmp_motor_num3 = motor_Failure_Number_3;
screen_msg_flag3 = 0;
}
}
else if (motor_Failure_Number_3 == 0 && motor_number_ == tmp_motor_num3 - 1)
{
if (!screen_msg_flag3)
{
// motor_constant_ = kDefaultMotorConstant;
std::cout << "Motor number [" << tmp_motor_num3 << "] running! [Motor thrust = (default)]" << std::endl;
screen_msg_flag3 = 1;
}
}
}
// typedef const boost::shared_ptr<const physics_msgs::msgs::Wind> WindPtr;
// 여기 msg에는 gazebo_wind_plugin에서 pub되는 wind_msg이다.
void GazeboMotorModel::WindVelocityCallback(WindPtr &msg)
{
wind_vel_ = ignition::math::Vector3d(msg->velocity().x(),
msg->velocity().y(),
msg->velocity().z());
// std::cout << "[wind_vel_] : (" << wind_vel_.X() << ", " << wind_vel_.Y() << ", " << wind_vel_.Z() << ")" << std::endl;
// 이렇게 출력하는 이유는 << 연산자가 ignition::math::Vector3d 타입의 변수를 한번에 출력하는 방법이 정의 되어 있지 않아서이다.
/*
wind_vel_ += ignition::math::Vector3d(0.1,0,0);
std::cout << "[wind_vel_] : (" << wind_vel_.X() << ", " << wind_vel_.Y() << ", " << wind_vel_.Z() << ")" << std::endl;
*/
// 이거 되는듯?
}
GZ_REGISTER_MODEL_PLUGIN(GazeboMotorModel);
}
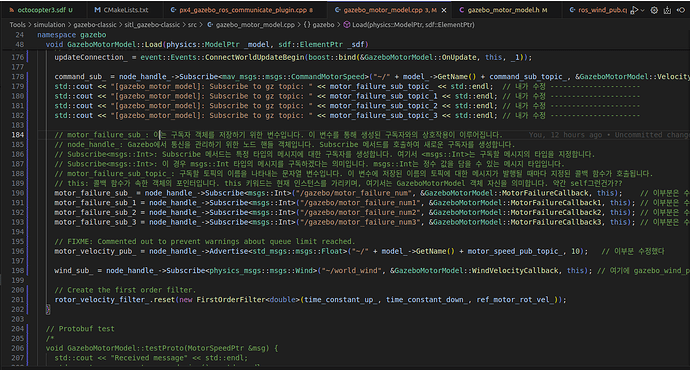
The code above is in the path
/home/hmcl/PX4_testbed/PX4-Autopilot/Tools/simulation/gazebo-classic/sitl_gazebo-classic/src/gazebo_motor_model.cpp
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <std_msgs/Float64.h>
#include <gazebo/transport/transport.hh>
#include <gazebo/gazebo_client.hh>
#include <gazebo/msgs/msgs.hh>
#include <iostream>
// 전역 변수로 ROS 메시지 선언
std_msgs::Float64 my_motor_velocity;
// 콜백 함수: 수신된 메시지를 처리
void motorVelocitySubCallback(const boost::shared_ptr<const gazebo::msgs::Any> &msg)
{
if (msg->has_double_value()) // 메시지에 double 값이 있는지 확인
{
my_motor_velocity.data = msg->double_value();
ROS_INFO("Received motor velocity: %f", my_motor_velocity.data);
}
else
{
ROS_WARN("Received a message that does not contain a double value.");
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// Gazebo transport 초기화
gazebo::client::setup(argc, argv);
// Gazebo 노드 생성 및 초기화
gazebo::transport::NodePtr node_handle(new gazebo::transport::Node());
node_handle->Init();
// Gazebo 토픽 구독 및 콜백 함수 등록
gazebo::transport::SubscriberPtr motor_velocity_sub = node_handle->Subscribe("/gazebo/default/octocopter3/motor_speed/0", motorVelocitySubCallback);
// ROS 초기화
ros::init(argc, argv, "motor_velocity_pub", ros::init_options::NoSigintHandler);
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Publisher motor_velocity_pub = nh.advertise<std_msgs::Float64>("/my/octocopter3/motor_speed", 10);
ros::Rate loop_rate(10);
// 무한 루프: Gazebo 메시지를 지속적으로 수신하고 ROS로 퍼블리시
while (ros::ok())
{
motor_velocity_pub.publish(my_motor_velocity); // ROS 메시지 퍼블리시
ros::spinOnce(); // ROS 콜백 처리
loop_rate.sleep(); // 루프 주기 대기
}
// Gazebo 종료
gazebo::client::shutdown();
return 0;
}
This code is before px4_gazebo_ros_communicate_plugin.cpp is made like a plugin.
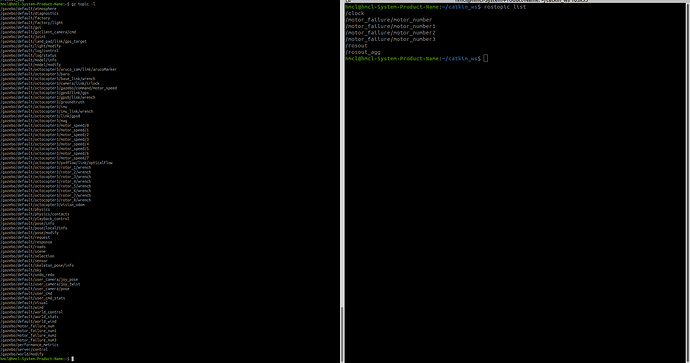
When I run make px4_sitl gazebo-classic_octocopter3, I believe the publisher motor_velocity_pub_ is publishing to the Gazebo topic /gazebo/default/octocopter3/motor_speed/*.
Therefore, I created a C++ file in my catkin_ws to subscribe to the Gazebo topic /gazebo/default/octocopter3/motor_speed/*. The code file I created is px4_gazebo_ros_communicate_plugin.cpp. However, when I check the topic list, I don’t see the topic I want.
I realized something is wrong, and I have a few questions:
- Is there a way to receive a Gazebo topic (using
gazebo::transport::NodePtr node_handle(new gazebo::transport::Node());) as a ROS topic? - Can Gazebo topics only be exchanged within plugins? If so, do I need to create another plugin file in the path
/home/hmcl/PX4_testbed/PX4-Autopilot/Tools/simulation/gazebo-classic/sitl_gazebo-classic/src? - Is it not possible to receive Gazebo topics from within the code written in
catkin_ws?
I might not fully understand some parts because I am using GPT for translation. Any feedback would be appreciated!